1. Kmeans
数据:自己产生的三维数据,分别围绕正方形的8个顶点
{0, 0, 0}, {0, 10, 0}, {0, 0, 10}, {0, 10, 10},
{10, 0, 0}, {10, 0, 10}, {10, 10, 0}, {10, 10, 10}

程序逻辑:
读取HDFS上的block到内存,每个block转化为RDD,里面包含vector。
然后对RDD进行map操作,抽取每个vector(point)对应的类号,输出(K,V)为(class,(Point,1)),组成新的RDD。
然后再reduce之前,对每个新的RDD进行combine,在RDD内部算出每个class的中心和。使得每个RDD的输出只有最多K个KV对。
最后进行reduce得到新的RDD(内容的Key是class,Value是中心和,再经过map后得到最后的中心。
先上传到HDFS上,然后在Master上运行
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.SparkKMeans
master@master:5050 hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/Kmeans/Square-10GB.txt 8 2.0
|
迭代执行Kmeans算法。
一共160个task。(160 * 64MB = 10GB)
利用了32个CPU cores,18.9GB的内存。
每个机器的内存消耗为4.5GB (共40GB)(本身points数据10GB*2,Map后中间数据(K, V) => (int, (vector, 1)) (大概10GB)

最后结果:
0.505246194 s
Final centers: Map(5 -> (13.997101228817169, 9.208875044622895, -2.494072457488311), 8 -> (-2.33522333047955, 9.128892414676326, 1.7923150585737604), 7 -> (8.658031587043952, 2.162306996983008, 17.670646829079146), 3 -> (11.530154433698268, 0.17834347219956842, 9.224352885937776), 4 -> (12.722903153986868, 8.812883284216143, 0.6564509961064319), 1 -> (6.458644369071984, 11.345681702383024, 7.041924994173552), 6 -> (12.887793408866614, -1.5189406469928937, 9.526393664105957), 2 -> (2.3345459304412164, 2.0173098597285533, 1.4772489989976143))
|
50MB/s 10GB => 3.5min
10MB/s 10GB => 15min
|
在20GB的数据上测试

运行测试命令:
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.SparkKMeans master@master:5050
hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/Kmeans/Square-20GB.txt 8 2.0 | tee mylogs/sqaure-20GB-kmeans.log
|
得到聚类结果:
Final centers: Map(5 -> (-0.47785701742763115, -1.5901830956323306,
-0.18453046159033773),
8 -> (1.1073911553593858, 9.051671594514225, -0.44722211311446924),
7 -> (1.4960397239284795, 10.173412443492643, -1.7932911100570954),
3 -> (-1.4771114031182642, 9.046878176063172, -2.4747981387714444),
4 -> (-0.2796747780312184, 0.06910629855122015, 10.268115903887612),
1 -> (10.467618592186486, -1.168580362309453, -1.0462842137817263),
6 -> (0.7569895433952736, 0.8615441990490469, 9.552726007309518),
2 -> (10.807948500515304, -0.5368803187391366, 0.04258123037074164))
|
基本就是8个中心点
内存消耗:(每个节点大约5.8GB),共50GB左右。

内存分析:
20GB原始数据,20GB的Map输出
12/06/05 11:11:08 INFO spark.CacheTracker: Looking for RDD partition 2:302
12/06/05 11:11:08 INFO spark.CacheTracker: Found partition in cache!
|
在20GB的数据上测试(迭代更多的次数)
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.SparkKMeans master@master:5050 hdfs://master:900
0/user/LijieXu/Kmeans/Square-20GB.txt 8 0.8
|
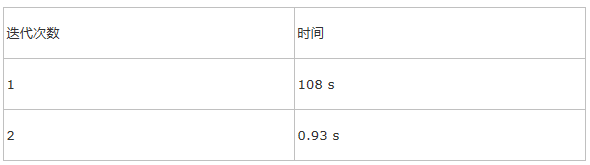
Task数目:320
时间:
迭代轮数对内存容量的影响:

2. HdfsTest
测试逻辑:
package spark.examples
import spark._
object HdfsTest {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val sc = new SparkContext(args(0), "HdfsTest")
val file = sc.textFile(args(1))
val mapped = file.map(s => s.length).cache()
for (iter <- 1 to 10) {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
for (x <- mapped) { x + 2 }
// println("Processing: " + x)
val end = System.currentTimeMillis()
println("Iteration " + iter + " took " + (end-start) + " ms")
}
}
}
|
首先去HDFS上读取一个文本文件保存在file
再次计算file中每行的字符数,保存在内存RDD的mapped中
然后读取mapped中的每一个字符数,将其加2,计算读取+相加的耗时
只有map,没有reduce。
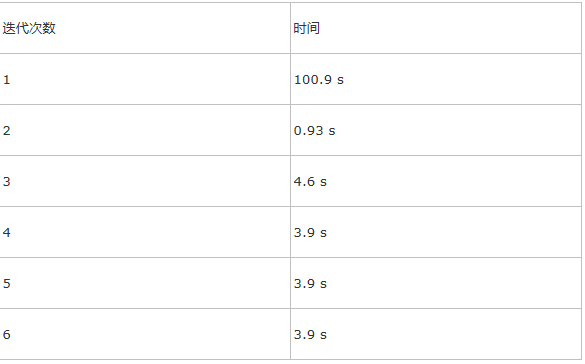
测试10GB的Wiki
实际测试的是RDD的读取性能。
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.HdfsTest master@master:5050
hdfs://master:9000:/user/LijieXu/Wikipedia/txt/enwiki-20110405.txt
|
测试结果:
Iteration 1 took 12900 ms = 12s
Iteration 2 took 388 ms
Iteration 3 took 472 ms
Iteration 4 took 490 ms
Iteration 5 took 459 ms
Iteration 6 took 492 ms
Iteration 7 took 480 ms
Iteration 8 took 501 ms
Iteration 9 took 479 ms
Iteration 10 took 432 ms
|
每个node的内存消耗为2.7GB (共9.4GB * 3)
基本没有什么影响,主要内存消耗:20GB的输入数据RDD,20GB的中间数据。
Final centers: Map(5 -> (-4.728089224526789E-5, 3.17334874733142E-5, -2.0605806380414582E-4),
8 -> (1.1841686358289191E-4, 10.000062966002101, 9.999933240005394), 7 -> (9.999976672588097,
10.000199556926772, -2.0695123602840933E-4),
3 -> (-1.3506815993198176E-4, 9.999948270638338, 2.328148782609023E-5),
4 -> (3.2493629851483764E-4, -7.892413981250518E-5, 10.00002515017671), 1 -> (10.00004313126956, 7.431996896171192E-6,
7.590402882208648E-5), 6 -> (9.999982611661382, 10.000144597573051, 10.000037734639696),
2 -> (9.999958673426654, -1.1917651103354863E-4, 9.99990217533504))
|
结果可视化


实际测试的是RDD的读取性能。
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.HdfsTest master@master:5050
hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/Wikipedia/txt/enwiki-20110405.txt
|
测试90GB的RandomText数据
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run spark.examples.HdfsTest master@master:5050
hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/RandomText90GB/RandomText90GB
|
耗时:
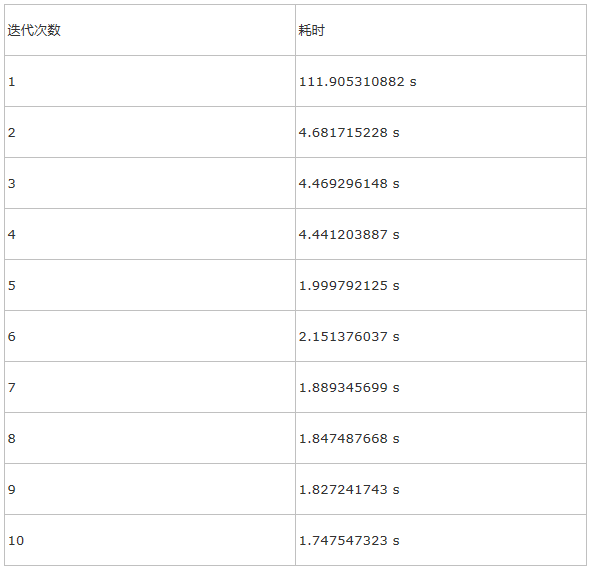
内存总消耗30GB左右。
单个节点的资源消耗:

3. 测试WordCount
写程序:
import spark.SparkContext
import SparkContext._
object WordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <master> <jar>")
System.exit(1)
}
val sp = new SparkContext(args(0), "wordcount", "/opt/spark", List(args(1)))
val file = sp.textFile("hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/Wikipedia/txt/enwiki-20110405.txt");
val counts = file.flatMap(line => line.split(" ")).map(word => (word, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9000/user/Output/WikiResult3")
}
}
|
打包成mySpark.jar,上传到Master的/opt/spark/newProgram。
运行程序:
root@master:/opt/spark# ./run -cp newProgram/mySpark.jar WordCount master@master:5050 newProgram/mySpark.jar
|
Mesos自动将jar拷贝到执行节点,然后执行。
内存消耗:(10GB输入file + 10GB的flatMap + 15GB的Map中间结果(word,1))
还有部分内存不知道分配到哪里了。
耗时:50 sec(未经过排序)
Hadoop WordCount耗时:120 sec到140 sec
结果未排序
单个节点:

Hadoop测试
Kmeans
运行Mahout里的Kmeans
root@master:/opt/mahout-distribution-0.6# bin/mahout org.apache.mahout.clustering.
syntheticcontrol.kmeans.Job -Dmapred.reduce.tasks=
36 -i /user/LijieXu/Kmeans/Square-20GB.txt -o output -t1 3 -t2 1.5 -cd 0.8 -k 8 -x 6
|
在运行(320个map,1个reduce)
Canopy Driver running buildClusters over input: output/data
时某个slave的资源消耗情况

Completed Jobs

运行多次10GB、20GB上的Kmeans,资源消耗


Hadoop WordCount测试


Spark交互式运行
进入Master的/opt/spark
运行
MASTER=master@master:5050 ./spark-shell
|
打开Mesos版本的spark
在master:8080可以看到framework
Active Frameworks
scala> val file = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9000/user/LijieXu/Wikipedia/txt/enwiki-20110405.txt")
scala> file.first
scala> val words = file.map(_.split(' ')).filter(_.size < 100) //得到RDD[Array[String]]
scala> words.cache
scala> words.filter(_.contains("Beijing")).count
12/06/06 22:12:33 INFO SparkContext: Job finished in 10.862765819 s
res1: Long = 855
scala> words.filter(_.contains("Beijing")).count
12/06/06 22:12:52 INFO SparkContext: Job finished in 0.71051464 s
res2: Long = 855
scala> words.filter(_.contains("Shanghai")).count
12/06/06 22:13:23 INFO SparkContext: Job finished in 0.667734427 s
res3: Long = 614
scala> words.filter(_.contains("Guangzhou")).count
12/06/06 22:13:42 INFO SparkContext: Job finished in 0.800617719 s
res4: Long = 134
|
由于GC的问题,不能cache很大的数据集。